Unlocking the Potential of THC-A
21st Sep 2023
Title: Unlocking the Potential of THC-A: The Non-Psychoactive Powerhouse
When we think of cannabis, we often associate it with the well-known compound THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) responsible for the plant's psychoactive effects. However, there's another, lesser-known cannabinoid that has been quietly making waves in the world of cannabis and wellness. Enter THC-A (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), a non-psychoactive compound with intriguing therapeutic potential. In this blog post, we'll explore THC-A, its properties, and why it's gaining attention in the world of cannabinoids.
What Is THC-A?
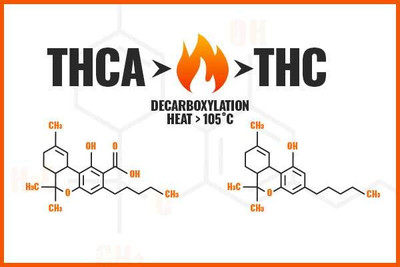
THC-A is a precursor to THC, meaning it's the acidic form of THC found in raw, unheated cannabis. Unlike THC, THC-A doesn't produce the characteristic "high" associated with cannabis consumption. Instead, it offers a range of potential health benefits without the psychoactive effects.
The Potential Benefits of THC-A:
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Research suggests that THC-A may have anti-inflammatory properties, making it a potential option for managing conditions characterized by inflammation, such as arthritis or Crohn's disease.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Some studies have shown that THC-A may protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain.
- Nausea and Vomiting Relief: THC-A has shown promise in alleviating nausea and vomiting, particularly in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
- Appetite Stimulation: Like THC, THC-A may stimulate appetite, making it beneficial for individuals struggling with conditions that cause appetite loss or wasting syndrome.
- Pain Management: Preliminary research suggests that THC-A may have analgesic properties, making it a potential option for pain management.
- Anti-Tumor Properties: Some studies have explored the anti-tumor potential of THC-A, but more research is needed to fully understand its effects on cancer cells.
How to Use THC-A:
THC-A is typically found in raw or unheated cannabis, such as fresh cannabis leaves or buds. While consuming raw cannabis may not be appealing due to its strong, earthy taste and limited availability, there are a few ways to incorporate THC-A into your wellness routine:
- Juicing: Juicing fresh cannabis leaves or buds is one way to consume THC-A. This method provides a concentrated source of cannabinoids without the psychoactive effects of THC.
- Supplements: Some companies offer THC-A supplements, which can be a more convenient and controlled way to add this cannabinoid to your wellness regimen.
- Topical Products: THC-A-infused topical products like creams and balms are available and may be useful for localized relief from pain or inflammation.
Caution and Legal Considerations:
It's essential to note that the legal status of THC-A can vary from one jurisdiction to another. Always check your local laws and regulations before using THC-A products.
In Conclusion:
While THC-A may not receive the same attention as its psychoactive counterpart THC, its potential health benefits are certainly worth exploring. As researchers continue to delve into the properties and therapeutic applications of THC-A, we may uncover even more reasons to appreciate this non-psychoactive cannabinoid. Whether you're seeking relief from a specific condition or simply curious about the diverse world of cannabinoids, THC-A is a fascinating compound worth keeping an eye on as it continues to unlock its potential in the world of wellness.